Peregrine Falcon
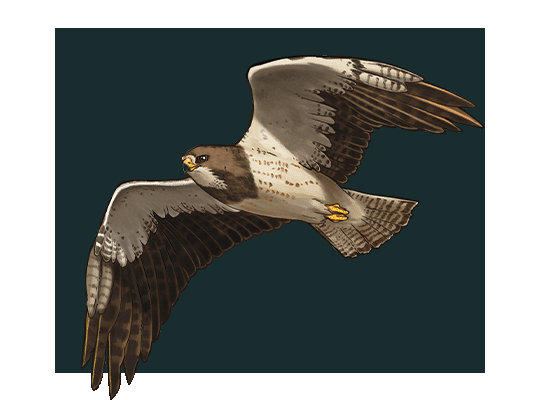
This is the most famous species in North America saved from the brink of extinction. This incredible success was engineered by The Peregrine Fund, which is based in Boise. Peregrine falcons hold the record for the fastest animal on Earth, with diving speeds recorded at more than 200 miles per hour. They are most apt to be found around wetlands and coasts where cliffs provide nesting sites, but they have also adopted tall buildings as suitable nest sites. Adult peregrines have a dark vertical bar on the face and lack the underwing pattern of the prairie falcon.